Public vs. private vs. hybrid cloud: The key differences in cloud computing

This in-depth guide will delve into the key distinctions between the most prominent cloud computing models: public, private, and hybrid. By the end, you’ll have the necessary insights to make an informed decision tailored to your organization's distinctive needs and aspirations.
Cloud computing represents more than just a shift in an organization’s IT infrastructure; it's a transformative force that has reshaped the way organizations operate, innovate, and serve their customers. It offers a myriad of benefits, including scalability, agility, and cost savings.
However, with so many different cloud computing models available, it can be difficult to know which option is right for your business.
Read on to discover which cloud computing paradigm holds the key to unlocking your business's full potential, and my no. 1 recommendation.
Understanding the basics of cloud deployment
Before diving into which cloud model to choose, you must first learn the difference between cloud computing and cloud deployment.
Cloud computing is a broad term that encompasses all aspects of delivering IT resources and applications over the internet (“the cloud”), such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. This is made possible via cloud services such as Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
By allowing businesses to access on-demand IT resources and applications without having to build and maintain their own infrastructure, cloud computing facilitates faster innovation and economies of scale. That’s why up to 60% of the world's corporate data is now stored and processed in the cloud.
Cloud deployment, on the other hand, is a specific process within cloud computing that focuses on getting applications and workloads up and running in the cloud. It entails choosing a cloud deployment model (such as public cloud, private cloud, or hybrid cloud), provisioning the necessary resources, and configuring the application.
Unlike traditional computing, where everything is stored and processed on local servers or personal computers, cloud deployment relies on remote servers hosted and operated by cloud service providers such as Liquid Web, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Public vs. private vs. hybrid: A comparative analysis
Among the various cloud deployment models, three prominent options stand out: public, private, and hybrid clouds. Each offers a distinct approach to harnessing the power of the cloud, catering to unique organizational needs and requirements.
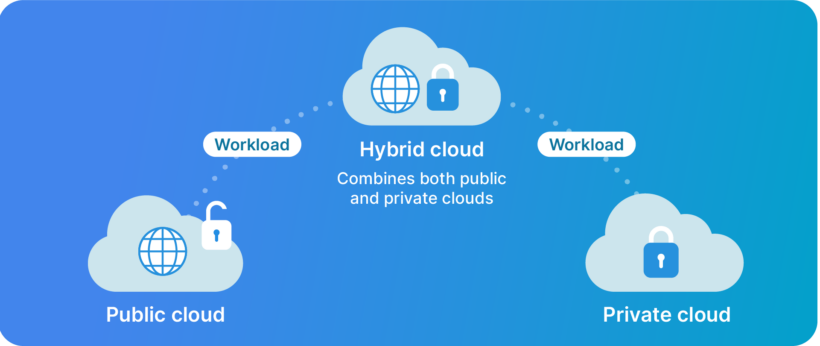
Public cloud
Public clouds, the most common type of cloud computing, are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers. It provides virtualized resources and services that are typically shared by multiple customers or organizations over the public internet.
Public clouds offer a level of scalability and accessibility unparalleled by other models. Resources can be provisioned or de-provisioned on demand, allowing businesses to respond dynamically to fluctuating workloads.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing model: The financial flexibility of the public cloud is especially beneficial for startups and small businesses. This cost structure allows organizations to avoid the upfront capital expenses associated with traditional on-premises infrastructure. Instead, they pay only for the resources they actually consume. | Trade-off in terms of customization and control: Organizations must operate within the confines of the cloud provider's infrastructure and security policies, which may not align perfectly with their unique needs. |
| Pre-built services and solutions: Offerings like databases, machine learning tools, and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) expedite development cycles and reduce the complexity of managing the underlying infrastructure. | Security vulnerabilities: While providers implement robust security measures, the multi-tenant nature of public clouds means that organizations share the same underlying hardware and network infrastructure. Consequently, stringent security practices, such as encryption and access controls, are paramount to safeguard data and prevent unauthorized access. |
Public clouds can be an apt choice for businesses that value quick and flexible scalability without control privileges over configurations and security.
Private cloud
Private clouds represent a realm of control and exclusivity. It is a cloud computing environment that is dedicated to a single organization hosted on-premises or in a data center managed by a third-party provider.
This isolation offers a higher degree of control over infrastructure, security, and compliance, making private clouds an attractive choice for enterprises with stringent regulatory requirements or sensitive data.
Private clouds offer more control and security than public clouds, but they are also more expensive.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Customization: Private clouds excel in providing customization and tailoring resources to meet specific business needs. Organizations can fine-tune the infrastructure to optimize performance, allocate resources based on application requirements, and implement stringent security protocols tailored to their unique risk profiles. | Costs more than public clouds: Instead of the variable costs associated with pay-as-you-go pricing, private clouds typically involve fixed costs for hardware, software, and maintenance. While this predictability can simplify budgeting, it also requires a significant upfront investment, making private clouds less accessible for smaller organizations or startups. |
| High data security control: This model caters to regulatory environments requiring high protection levels because it puts security control in the hands of the company. | Maintenance: Private clouds come with the challenge of managing and maintaining the entire infrastructure stack. Organizations must procure, deploy, and manage hardware and software components, which demands a skilled IT team and ongoing operational expenses. This can be resource-intensive and time-consuming, detracting from the organization's focus on core business objectives. |
| Limited scalability: While private clouds offer scalability, private clouds depend on the company’s initial investment in resources and infrastructure. |
Private clouds are particularly advantageous for industries like finance and healthcare, where data privacy and regulatory compliance are paramount.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud is a combination of public and private cloud services. It allows organizations to keep their most sensitive data and applications in a private cloud while using the public cloud for less sensitive workloads.
Hybrid clouds can offer the best of both worlds in terms of cost, security, and flexibility.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Scalability and cost-effectiveness: Organizations can harness the scalability and cost-efficiency of public clouds for non-sensitive workloads or burst capacity while keeping mission-critical applications and sensitive data within the confines of a private cloud for enhanced security and control. | Management: Implementing a hybrid cloud strategy necessitates robust management and orchestration tools to seamlessly connect and coordinate resources across disparate environments. |
| Business continuity and disaster recovery capabilities: In the event of a data center outage or other unforeseen disruptions, critical workloads can be quickly shifted to the public cloud, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss. | Compatibility and interoperability: Compatibility and interoperability challenges may arise due to differences in technology stacks between public and private clouds. |
The duality of hybrid clouds is particularly beneficial for businesses with dynamic workloads that experience periodic spikes in resource demand.
To sum it up, here are the key differences between public, private, and hybrid clouds:
| Feature | Public cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Hosted by a third-party cloud provider. | Hosted on-premise or in a data center managed by a third-party provider. | A combination of public and private cloud approaches. |
| Access | Accessed over the public internet. | Accessed over a private network. | Accessed over the public internet and/or a private network. |
| Cost | Typically the most cost-effective option. | Typically the most expensive option. | Cost varies depending on the mix of public and private cloud services. |
| Security | Less secure than a private cloud. | Most secure out of the three models. | Security varies according to the setup of the public and private cloud infrastructures. |
| Flexibility | Highly scalable. | Less scalable than the public cloud. | Scalability depends on the use of the public cloud. |
Ultimately, adopting the right cloud deployment model should align with an organization's strategic vision, regulatory requirements, and budgetary considerations. Businesses must continually assess their needs to harness the full potential of their cloud models.
Real-world applications of cloud models
Real-world public cloud use cases
Example 1: Tech startup
Tech startup companies often face the dilemma of having limited capital but the potential for rapid growth. Hosting their web applications on public cloud platforms, such as Liquid Web or Amazon Web Services (AWS), allows them to overcome this challenge.
These platforms offer a pay-as-you-go model, which means startups can scale their resources in real time based on user demand. This scalability ensures that they can handle traffic spikes and growth without the burden of hefty infrastructure investments.
Example 2: Big ecommerce platforms
For ecommerce giants, holidays and seasonal sales events often result in unpredictable surges in website traffic. Overprovisioning infrastructure to accommodate these spikes can be costly and inefficient.
To address this challenge, many ecommerce companies opt for public cloud solutions like Liquid Web or Microsoft Azure. Their elasticity allows online stores to seamlessly scale resources during peak seasons, ensuring a smooth shopping experience for customers without unnecessary infrastructure expenses.
Real-world private cloud use cases
Example 1: Financial services corporation
Financial services entities deal with sensitive customer data and strict regulatory requirements. To maintain compliance and enhance data security, they often opt for private cloud solutions.
Building a private cloud on-premises or through a dedicated provider offers complete control over data access and security measures. This ensures that financial data remains confidential and protected, meeting regulatory standards while delivering the necessary services to clients.
Example 2: Government agency
Government agencies handle classified information that demands the highest level of security and control. To address these unique requirements, government entities often deploy private cloud infrastructures. These private clouds offer the ability to maintain strict control over data access and encryption, ensuring that classified documents and communications remain confidential and secure.
Real-world hybrid cloud use cases
Example 1: Healthcare provider
Healthcare providers need to balance the security of patient data with the need for remote access, especially in the era of telemedicine. A hybrid cloud strategy allows them to achieve this balance.
Sensitive patient data can be stored on a private cloud, ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations, while telemedicine applications can run on a public cloud, enabling remote access for healthcare professionals and patients.
Example 2: Manufacturing company
Manufacturing companies rely on real-time data from IoT devices to optimize production processes. A hybrid cloud approach allows them to collect and process this data efficiently.
Real-time IoT data can be stored and analyzed on a public cloud, providing scalability and processing power, while sensitive production data remains on a private cloud, ensuring control and security over critical operations.
The real-world examples highlighted above demonstrate the versatility of cloud computing models in addressing various business challenges. Whether it's enabling rapid growth for startups, ensuring data security and compliance in the financial sector, or facilitating remote access in healthcare, cloud solutions offer tailored approaches to meet diverse needs.
As you consider your own business or industry-specific challenges, consulting Liquid Web and harnessing their cloud solutions could be the key to unlocking new possibilities for your organization.
Cost and pricing considerations for different cloud models
Understanding the financial implications associated with each cloud model is vital for businesses to make an informed decision. This entails an awareness of the range of costs, from upfront charges and persistent fees to possible unexpected expenses.
A significant proportion of businesses' total cloud expenses – ranging from 26% to 50% – is allocated to cloud storage. This insight underscores the importance of evaluating the cost-effectiveness of cloud models and their services.
Moreover, insightful data from a three-year comparative study between public and private clouds unveils eye-opening findings:
- The accumulated cost for the public cloud stands at approximately $1,092,188.06.
- Private cloud procurement adds up to approximately $578,893.34, which is significantly lower than its public counterpart.
- A considerable difference of roughly $2000/month encourages a shift towards private cloud usage, particularly for large businesses for whom the savings would be most impactful.
This data suggests that private cloud solutions can be more cost-effective in the long term, with an approximate monthly difference of $2,000 in favor of private cloud options. This could be due to the rise in costs of public cloud services, which is leading to concerns among Chief Information Officers (CIOs).
For instance, Vagesh Dave, CIO of McDermott International, openly mentioned his switch from public to private cloud resources due to their lower costs in the long haul. This could indicate a trend in adopting private cloud solutions among businesses seeking more budget-friendly alternatives.
It’s also important to note that the cost trajectory for each cloud model varies substantially based on the business scale and size.
The good news: there are a multitude of services available for those pursuing transparent and cost-effective cloud solutions, such as Liquid Web’s cloud server hosting and VMware private cloud.
Both solutions exemplify Liquid Web’s commitment to providing price transparency and eliminating additional per-VM fees to provide reliable solutions for businesses aiming to streamline their cloud services.
Choosing the right cloud strategy for your business
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It's essential to make your decision based on several key considerations specific to your operation, like:
- The size of the business: In many instances, larger enterprises may have the resources to uphold a more private and secure cloud, while smaller companies often benefit from the cost-effectiveness and ease of access that public clouds provide.
- The industry: Strict regulations surround data confidentiality in sectors like finance or health services, making private clouds a likely option. On the other hand, a startup in the tech industry might lean towards the scalability and low upfront costs of a public cloud.
- Regulatory requirements: If your business is obliged to adhere to specific data handling rules, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), it might make the most sense to opt for a private or hybrid cloud.
Liquid Web recognizes and embraces the unique needs and differences among businesses, offering customizable cloud solutions designed to cater to a wide range of needs. Even better, Liquid Web provides a complimentary migration service to ensure a smooth transition with minimal downtime.
Now that you have a clear understanding of the different cloud models, it’s time for the transition. Here are the steps:
- Assess your business needs: Identify your business objectives and how they align with cloud computing. Evaluate your data, applications, and workloads to decide what can be moved to the cloud.
- Select a cloud model: Following your assessment, decide on the most suitable cloud model for your operations. Consider key elements such as cost, scalability, security, and customizability.
- Implement the cloud model: Implementation involves preparing your existing systems for the transition and then initiating the migration. Depending on your specific needs, it may require a complete shift of your IT infrastructure to the cloud or just moving specific workloads. Liquid Web offers a complimentary migration service to ensure a smooth transition with minimal downtime.
- Monitor performance: It's crucial to regularly monitor your cloud services after implementation to ensure they deliver the expected performance. With Liquid Web, you'll have access to advanced monitoring solutions to troubleshoot any potential issues quickly.
Action plan: Your next steps in cloud migration
Embarking on a cloud migration journey can be a transformative experience for your business, but it also comes with its challenges. That’s where I recommend Liquid Web!
Liquid Web’s customer support (available 24/7/365) and expert team will handle the migration process for you, ensuring minimal disruption to your operations and data integrity. They’ll also monitor, optimize, and secure your cloud resources, allowing you to concentrate on your core business objectives.
Don't let the complexities of cloud migration hold your business back. Liquid Web is here to guide you through the process, from start to finish. Whether you're considering a public, private, or hybrid cloud solution, Liquid Web has the expertise and resources to make your transition smooth and efficient.
Take the first step towards unlocking the potential of the cloud for your business, and contact Liquid Web today for a consultation!